Advertisement
There's a quiet shift happening in how data is stored and explored. It's not about stuffing things into rows and columns anymore. When you want to connect dots—people, events, devices, pages—a regular database feels stiff. That's where graph databases come in. They store data more like how we think. Entities and relationships. Nodes and edges.
Open-source options lead this shift because they give developers control, flexibility, and freedom to build without worrying about licenses or vendor lock-in. Here's a closer look at nine solid open-source graph databases worth knowing.
Neo4j is the most well-known graph database in the open-source world. It's been around for over a decade and is used by companies and solo developers. The community edition is open source under GPLv3. You can use it to build small to medium-graph applications. It comes with its graph query language, Cypher, which reads a lot like simple English.
Neo4j makes working with relationships feel natural. It handles the connections well if you're mapping social networks, fraud detection models, or knowledge graphs. It's not as fast as some in large-scale environments, and enterprise features like clustering and fine-grained access controls are behind a paywall—but for most basic needs, it's rock-solid.
ArangoDB is a multi-model database, but its graph features are no afterthought. It supports both property graphs and RDF-style graphs. You can mix document and key/value data with graphs in one system. This gives you more room to design how your data works together.

It uses a query language called AQL (ArangoDB Query Language), which handles joins and traversals well. If you're building a project that switches between graph logic and regular document-based logic, ArangoDB keeps things flexible. It’s written in C++ and has good performance for most real-world cases.
OrientDB is another multi-model system. It handles graph, document, object, and key/value data types. You don't need to bolt systems together—it lets you model complex data structures natively. It supports SQL-style querying with extra syntax for graph traversal, making the learning curve easier if you come from relational databases.
It's good for projects like customer data platforms or product catalogs, where items are deeply connected but need traditional storage features. It's open source under Apache 2.0 and has been around long enough to be stable and tested.
Dgraph is built for speed. It's designed to scale horizontally and work well under heavy loads. The entire architecture is optimized for performance with large, complex graphs. It uses GraphQL+- as its query language, an extension of GraphQL that allows for deep filtering and traversal.
Dgraph is written in Go, which gives it a small footprint and fast execution. It is open source under the Apache 2.0 license. If you're working on a recommendation engine, real-time app, or analytics system that depends on fast reads and writes, Dgraph is a strong choice.
JanusGraph is a distributed graph database built to work with backend systems like Apache Cassandra, HBase, or Google Bigtable. It doesn't store data independently—it delegates that to a backing store. That makes it more complex to set up, but it allows for big, scalable solutions.
It supports the Gremlin query language and plugs into the TinkerPop graph computing framework. It’s well-suited for knowledge graphs, fraud detection, and anything needing large-scale graph analytics. It’s licensed under Apache 2.0 and has support from companies like IBM and Amazon.
TigerGraph isn’t fully open source, but it offers a free and open developer edition that gives enough features for individual use or prototyping. It focuses on speed, scalability, and analytics. The query language, GSQL, is optimized for complex patterns and paths.

It’s known for handling massive graphs with billions of edges and keeping queries fast. You'll need to install it on Linux, and the learning curve is a bit steeper, but it delivers if you're building something that needs heavy-duty real-time analysis.
GraphDB focuses on RDF graphs and is built for semantic web applications. It supports SPARQL and handles ontologies, linked data, and metadata-heavy structures. It's more common in academic, government, and publishing domains where structured vocabularies are used.
The free edition is not fully open source but is available for non-commercial use. It's good for people working with RDF triples, reasoning engines, and other semantic data tools. If your project depends on strict knowledge representation, GraphDB brings the right tools.
RedisGraph adds graph capabilities to Redis. It's lightweight and fast, with built-in C focusing on performance. It supports a modified Cypher query language and uses matrix operations under the hood to speed things up.
Since it's a Redis module, it fits best in environments that already use Redis or need in-memory speed. You can't store massive datasets unless you have a lot of RAM, but RedisGraph is one of the fastest options for real-time querying and dashboards. It's open source under the BSD 3-Clause License.
HugeGraph is a newer player but already shows promise. It’s open source under the Apache 2.0 license and supports massive graphs. It works with various backends like MySQL, RocksDB, and HBase. It supports the Gremlin query language and offers RESTful APIs.
HugeGraph's goal is to make managing huge graphs easier, especially in cloud or hybrid environments. It has visualization tools and some decent admin features built in. While it's still maturing, it’s gaining traction in China and among developers looking for alternatives to Western-developed tools.
If you're building something where relationships matter more than tables—like recommendation systems, fraud detection, or network monitoring—graph databases give your data better structure. Open-source tools offer freedom to build and scale without licensing limits. Each database here takes a different approach. Some prioritize speed, others focus on flexibility, and others focus on handling massive datasets. There's no universal choice—the right one depends on how your data connects and how you want to work with it.
Advertisement
Understand what machine learning (ML) is, its major types, why it is so important, how it works, and more in detail here

A Nvidia AI-powered humanoid robot is now serving coffee to visitors in Las Vegas, blending advanced robotics with natural human interaction in a café setting

Discover how AI reshapes contact centers through automation, omnichannel support, and real-time analytics for better experiences
Tech giants respond to state-level AI policies, advocating for unified federal rules to guide responsible AI use.

How Toyota is developing AI-powered smart factory tools in partnership with technology leaders to transform production efficiency, quality, and sustainability across its plants

Discover why global tech giants are investing in Saudi Arabia's AI ecosystem through partnerships and incentives.
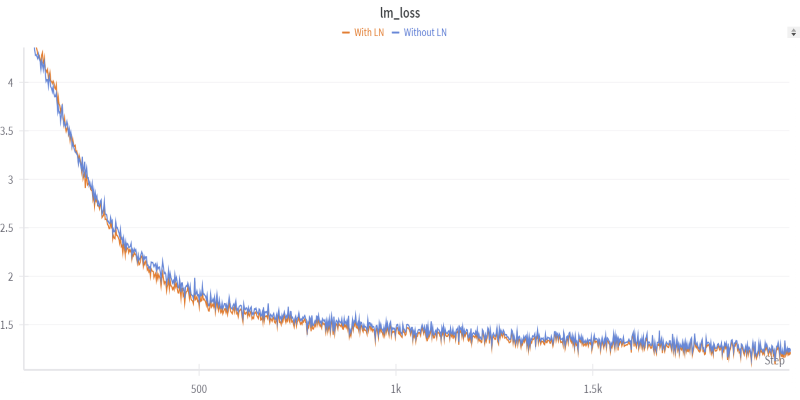
Want to shrink a large language model to under two bits per weight? Learn how 1.58-bit mixed quantization uses group-wise schemes and quantization-aware training

How AI in software development is transforming how developers write, test, and maintain code. Learn how artificial intelligence improves efficiency, automates repetitive tasks, and enhances software quality across every stage of the development process

Can AI actually make doctors’ jobs easier? Microsoft just launched its first AI assistant for health care workers—and it's changing the way hospitals function
Explore the key features, benefits, and top applications of OpenAI's GPT-4.1 in this essential 2025 guide for businesses.
How AI-powered genome engineering is advancing food security, with highlights and key discussions from AWS Summit London on resilient crops and sustainable farming

How to implement Policy Gradient with PyTorch to train intelligent agents using direct feedback from rewards. A clear and simple guide to mastering this reinforcement learning method