Advertisement
Tech competitions often blur together. They come and go, full of lofty themes and vague outcomes. But the AMD Pervasive AI Developer Contest steps into a very different space. It doesn’t just highlight who can code fastest or build the flashiest interface—it’s about solving real problems using AMD’s AI hardware and software stack. Whether you’re a student, an engineer, or someone who just enjoys experimenting with machine learning models, this contest is built to test what you can actually do with AI at the edge.
This year, AMD opened the doors to developers around the world with one simple challenge: build useful, original AI applications that run on AMD Ryzen AI or AMD Versal AI Edge platforms. There is no upper limit to ambition as long as the solution makes practical sense and runs reliably on AMD technology. It's not about building something just to show off—it's about building something that works.
The AMD Pervasive AI Developer Contest is judged on more than just functionality. Judges are not only evaluating whether the application works but also whether it works in a way that's practical, repeatable, and scalable. That might sound like a big ask, but in this context, it just means one thing: does the project solve a problem in a smart way using AMD AI tools?
There are two primary tracks—Ryzen AI and Versal AI Edge. The Ryzen AI track focuses on low-power AI use in consumer devices, like laptops or compact desktops. Versal AI Edge, on the other hand, targets high-throughput needs in edge computing, such as smart cameras, industrial automation, or medical devices. These aren't arbitrary lines. They're defined by the strengths of the platforms themselves.
Ryzen AI: Meant for inference workloads on local machines. Think about anything that can benefit from fast, private decision-making without relying on the cloud. Examples from past entries include gesture recognition systems, AI-based transcription, and localized language models running natively.
Versal AI Edge: More geared toward high-efficiency AI at the outermost edge of networks. These are the kinds of applications that monitor traffic patterns, detect defects in real time on factory lines, or provide advanced visual feedback in robotics.
The ideal entry doesn’t just show off what these platforms can do but what they should be doing out in the field.
Unlike contests that dump a problem statement and walk away, AMD supports developers throughout the process. You get access to actual development kits (depending on your submission and region), documentation, example code, and even mentorship opportunities. This isn’t about starting from scratch.
For Ryzen AI submissions, AMD offers support through tools like Vitis AI and ONNX runtime integrations. These help bridge the gap between raw ML models and deployable software. Participants are encouraged to build models with PyTorch or TensorFlow and then convert and optimize them for Ryzen's AI engine.
For Versal AI Edge, the development environment is a little more hardware-focused. You’re dealing with programmable logic and adaptable AI engines. AMD provides frameworks that help abstract some of that complexity—like the Vitis AI development stack. If you know how to train a model and want to see it run efficiently in edge use cases, you’ll find the right hooks here. All the backend support is already prepared, but the innovation part? That’s completely up to you.
Once the idea is ready, a structured process is in place to follow. This isn't a "submit on the last day and cross your fingers" kind of contest. AMD encourages early registration and active updates throughout the development phase. Here's how the process breaks down:

You fill out a short form describing your project idea. This includes which track you're entering, your proposed AI use case, and how you plan to execute it. The review panel then approves qualified entries for the build phase.
After approval, you begin developing your prototype. If your proposal is strong and feasible, AMD may provide hardware to support your build. This stage includes designing the model, integrating it with AMD’s platform, and testing real-world functionality. Regular check-ins aren’t mandatory, but they’re encouraged to ensure things stay on track.
You deliver a working proof-of-concept, including a demo video, source code, technical write-up, and deployment instructions. These are reviewed based on technical clarity, originality, usefulness, and how well they make use of AMD’s AI capabilities.
A panel of AMD engineers and AI experts evaluates the projects. Winners are chosen from each track, with separate prizes for standout innovation, community impact, and performance.
This process is straightforward and favors clarity over showmanship. If your idea makes sense and your execution is clean, you stand a strong chance.
Many developer contests offer vague rewards or questionable incentives. The AMD Pervasive AI Developer Contest keeps things grounded. Winners get cash prizes, AMD hardware, and high visibility across AMD’s platforms. That last part is often overlooked, but it can be just as valuable as the prize money itself—especially for independent developers or small teams looking to get their work seen.
If your project addresses a problem in healthcare, education, accessibility, or another high-impact area, it could also be highlighted in AMD's future developer spotlights or technical showcases.
The AMD Pervasive AI Developer Contest doesn't chase trends. It's not about creating another app that claims to do everything. It's about real-world AI that runs fast, runs locally, and solves something specific. Whether you're streamlining factory operations with Versal AI or building smart apps on a Ryzen-powered laptop, you're being asked to do one thing: build something useful and make it work well. The barrier to entry is low, but the bar for execution is high. And that’s exactly why this contest stands out.
Advertisement

Discover how ByteDance’s new AI video generator is making content creation faster and simpler for creators, marketers, and educators worldwide

How to write a custom loss function in TensorFlow with this clear, step-by-step guide. Perfect for beginners who want to create tailored loss functions for their models

Discover the top eight ChatGPT prompts to create stunning social media graphics and boost your brand's visual identity.

Can AI actually make doctors’ jobs easier? Microsoft just launched its first AI assistant for health care workers—and it's changing the way hospitals function

Learn how to boost sales with Generative AI. Learn tools, training, and strategies to personalize outreach and close deals faster

Explore seven advanced Claude Sonnet strategies to simplify operations, boost efficiency, and scale your business in 2025.

Discover powerful yet lesser-known ChatGPT prompts and commands that top professionals use to save time, boost productivity, and deliver expert results

Meta launches Llama 4, an advanced open language model offering improved reasoning, efficiency, and safety. Discover how Llama 4 by Meta AI is shaping the future of artificial intelligence
How AI-powered genome engineering is advancing food security, with highlights and key discussions from AWS Summit London on resilient crops and sustainable farming
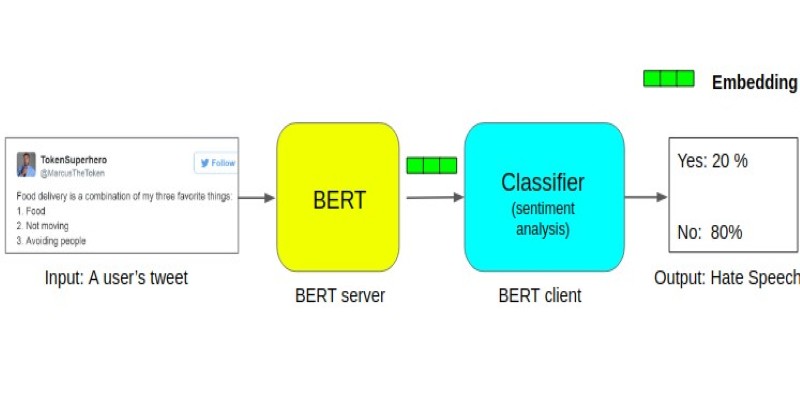
Learn about the BERT architecture explained for beginners in clear terms. Understand how it works, from tokens and layers to pretraining and fine-tuning, and why it remains so widely used in natural language processing

Why analytics is important for better outcomes across industries. Learn how data insights improve decision quality and make everyday choices more effective

Learn how to delete your ChatGPT history and manage your ChatGPT data securely. Step-by-step guide for removing past conversations and protecting your privacy