Advertisement
Reinforcement learning isn't magic. At its core, it's a process of making decisions based on rewards. But while the idea sounds straightforward, putting it into practice, especially with algorithms like Policy Gradient, can feel complex. Policy Gradient methods let agents learn directly from actions and rewards rather than building a model of the environment or estimating value functions.
With PyTorch, building and training these models becomes more accessible and transparent. In this article, we'll walk through the concept of Policy Gradient, understand how it works, and learn how to implement it using PyTorch. No unnecessary math clutter, just what you need to really understand it.
Policy Gradient methods belong to a category of reinforcement learning algorithms that learn a parameterized policy. This policy tells the agent what action to take, given a certain state. Unlike value-based methods, such as Q-learning, which aim to estimate the value of taking an action in a given state, Policy Gradient directly adjusts the policy to maximize the expected reward.
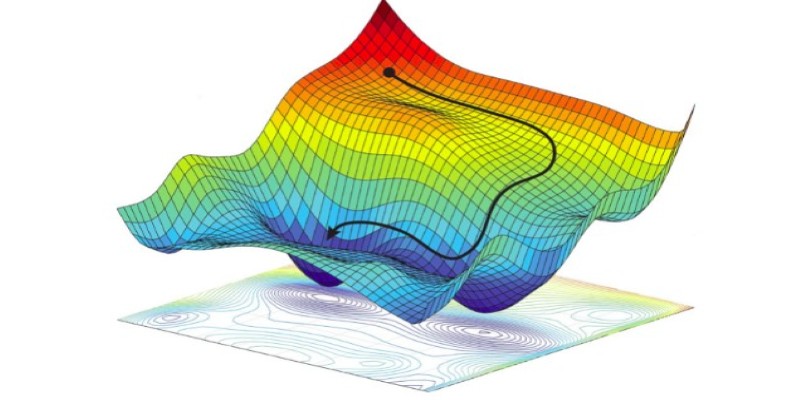
The “policy” here is a probability distribution over actions. The learning process aims to fine-tune this distribution so the agent tends to select actions that lead to higher long-term rewards. The key is in how we update the policy — that’s where the gradient comes in.
In technical terms, the goal is to maximize the expected return. The return is the total accumulated reward, possibly discounted over time. The algorithm tweaks the policy parameters using gradient ascent — moving them slightly in the direction that increases the probability of getting more reward. This idea is formalized using the Policy Gradient Theorem.
What makes Policy Gradient appealing is its ability to handle high-dimensional or continuous action spaces. This is important for tasks like robotic control or environments where the action space isn’t discrete or limited.
Let’s break down how Policy Gradient operates, especially using PyTorch. First, you need a policy network. This is usually a small neural network that takes the state of the environment and outputs probabilities for each possible action. You sample an action from this distribution, perform the action, get a reward, and observe the next state.
As the agent runs through the environment, it collects episodes. An episode is a full sequence of (state, action, reward) until the end of the task. Once an episode is complete, the algorithm goes back and calculates the return for each action taken. It then updates the policy network to make the good actions more probable and the poor ones less so.
PyTorch makes this process relatively smooth thanks to automatic differentiation. When you compute the loss, which is the negative log probability of the chosen action multiplied by the return, PyTorch handles the backpropagation for you.
Here’s a high-level overview of what the code does:
This simplicity in structure is one reason Policy Gradient is often the first reinforcement learning algorithm people implement.

Let’s walk through a simplified implementation using PyTorch. The example below uses a basic setup for a cart-pole balancing task, which is a classic environment available through OpenAI Gym.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import gym
class PolicyNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim):
super(PolicyNetwork, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(state_dim, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, action_dim),
nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
def select_action(policy_net, state):
state = torch.from_numpy(state).float().unsqueeze(0)
probs = policy_net(state)
action_dist = torch.distributions.Categorical(probs)
action = action_dist.sample()
return action.item(), action_dist.log_prob(action)
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.n
policy_net = PolicyNetwork(state_dim, action_dim)
optimizer = optim.Adam(policy_net.parameters(), lr=1e-2)
for episode in range(1000):
state = env.reset()
log_probs = []
rewards = []
done = False
while not done:
action, log_prob = select_action(policy_net, state)
state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
log_probs.append(log_prob)
rewards.append(reward)
# Calculate discounted returns
returns = []
G = 0
for r in reversed(rewards):
G = r + 0.99 * G
returns.insert(0, G)
returns = torch.tensor(returns)
returns = (returns - returns.mean()) / (returns.std() + 1e-9) # Normalize
loss = []
for log_prob, G in zip(log_probs, returns):
loss.append(-log_prob * G)
loss = torch.cat(loss).sum()
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
This code introduces most of the important parts: policy definition, action selection, reward accumulation, and policy update. You can expand this into more complex environments or improve it with techniques like entropy regularization or reward baseline subtraction to reduce variance.
Policy Gradient with PyTorch is one of the clearest ways to understand reinforcement learning. It's not about trying to be fancy with approximations or predictions — it's about learning behavior from feedback. The concept is simple: do something, see how well it works, and adjust to do better next time.
This method has been extended into more advanced algorithms like REINFORCE with baselines, Actor-Critic, and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). But at their heart, many of these keep the core idea of Policy Gradient: tweaking behaviour directly based on what worked.
PyTorch’s dynamic computation graph and clean syntax make it a natural fit for these tasks. It doesn’t hide the complexity, but it lets you build and debug easily, which is invaluable when experimenting or learning. For researchers and developers alike, this level of transparency helps build a real understanding of what’s happening during training.
Policy Gradient using PyTorch shows that learning to act doesn't have to be mysterious. The idea is clear: try actions, see how they turn out, and nudge your behaviour to be better. It's not flawless — high variance in rewards and slower convergence can be issues. But it forms the base for many powerful extensions that tackle those problems. PyTorch helps make the algorithm readable and manageable so you can focus on experimenting, testing, and learning. If you want to truly understand reinforcement learning, building a Policy Gradient model from scratch is a strong place to start.
Advertisement
Tech giants respond to state-level AI policies, advocating for unified federal rules to guide responsible AI use.
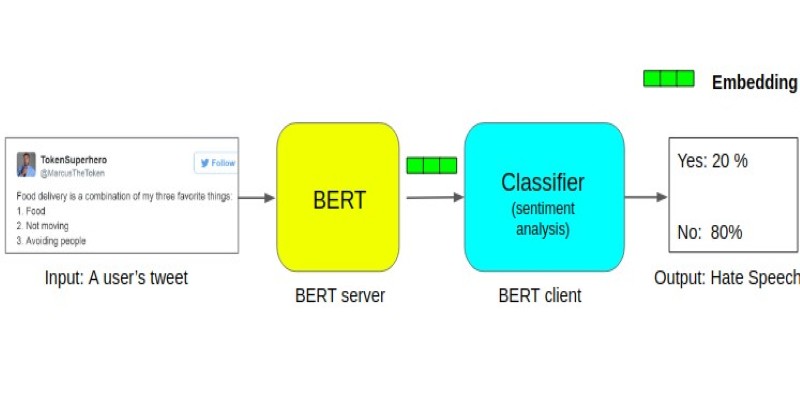
Learn about the BERT architecture explained for beginners in clear terms. Understand how it works, from tokens and layers to pretraining and fine-tuning, and why it remains so widely used in natural language processing

Why analytics is important for better outcomes across industries. Learn how data insights improve decision quality and make everyday choices more effective
How AI-powered genome engineering is advancing food security, with highlights and key discussions from AWS Summit London on resilient crops and sustainable farming
What loss functions are, why they matter, and how they guide machine learning models to make better predictions. A beginner-friendly explanation with examples and insights
Google debuts new tools and an agent protocol to simplify the creation and management of AI-powered agents.

How AI in software development is transforming how developers write, test, and maintain code. Learn how artificial intelligence improves efficiency, automates repetitive tasks, and enhances software quality across every stage of the development process

AI Trading is transforming the stock market by analyzing data, predicting trends, and executing smarter trades. Learn how artificial intelligence improves accuracy, manages risk, and reshapes modern investment strategies for both institutions and individual investors

Dynamic Speculation predicts future tokens in parallel, reducing wait time in assisted generation. Here’s how it works and why it improves speed and flow

Meta introduces Llama 4, intensifying the competition in the open-source AI model space with powerful upgrades.

Explore Apple Intelligence and how its generative AI system changes personal tech with privacy and daily task automation

Learn how to delete your ChatGPT history and manage your ChatGPT data securely. Step-by-step guide for removing past conversations and protecting your privacy