Advertisement
Wildfires are becoming more destructive as forests grow drier and hotter, putting lives, homes, and wildlife at risk. In response, scientists have developed an AI-driven wireless tree network that turns trees into sentinels. This system links trees with sensors, wireless communication, and artificial intelligence to detect fires early and predict how they’ll spread.
It creates a digital warning system embedded in the forest itself, sending alerts in real time. By giving trees a way to “speak” through technology, this approach offers a smarter, more timely defense against one of nature’s most unpredictable and devastating forces.
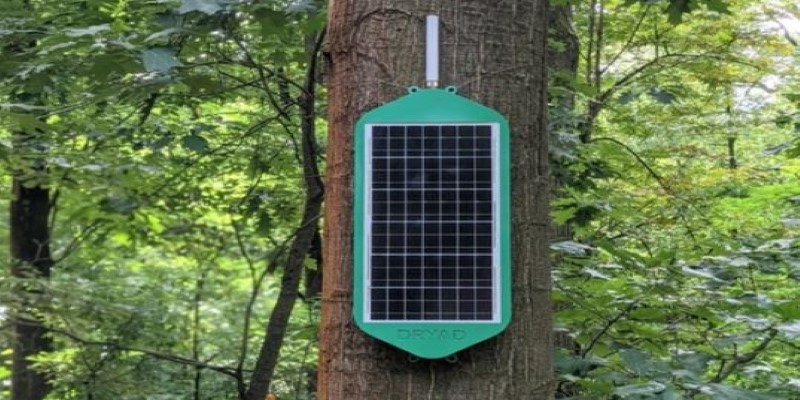
The network relies on compact sensors installed directly on trees, which measure critical environmental data such as temperature, wind speed, soil moisture, and even tiny traces of smoke in the air. Rather than transmitting this data to a distant tower or satellite, each sensor communicates wirelessly with the next, forming a web that covers miles of forest.
This mesh network is self-sustaining. Small solar panels or even bioelectric energy from the trees themselves power the sensors. Signals hop between nodes using low-energy, long-range technology that performs well even in rugged, isolated terrain where cellular service doesn’t reach. Every tree in the system becomes part of a distributed data grid, recording and transmitting local conditions continuously.
Thousands of these nodes work in unison to create a living map of the forest’s health and risk level. Data flows through the network to central hubs where it’s analyzed, providing instant insight into developing threats. The strength of this design lies in its redundancy—if one sensor fails or a section is damaged, the network simply routes around it, maintaining its coverage and function.
Artificial intelligence sits at the core of this wildfire defense system, interpreting the massive volume of data collected by the sensors. Forests are dynamic environments, and conditions can shift rapidly. AI excels at finding subtle signals in this complexity, identifying early signs of ignition or areas where a fire is most likely to intensify.
These AI models are trained on decades of wildfire records, learning how variables like slope, wind, humidity, and vegetation influence the way fires behave. Once the system detects conditions that match dangerous patterns, it sends targeted alerts to fire management teams. Rather than relying on human observation alone, this predictive capability allows responders to act faster and more strategically.
Another strength of AI is its ability to improve over time. With every fire it monitors, the system gains more knowledge, refining its predictions and reducing the number of false alarms. This learning process means that forests equipped with the network become better protected each season, with the AI adapting to local terrain and climate.
This approach blends seamlessly into natural landscapes. The sensors are unobtrusive and don’t harm the trees, soil, or surrounding wildlife habitats. Since they’re powered by renewable energy sources, they leave almost no ecological footprint and can operate continuously for years without intervention. There’s no need for disruptive construction, access roads, or clear-cutting to install the system.
For firefighting operations, the network offers improved accuracy and faster response times. Early warnings give crews the chance to contain fires before they escalate, often preventing the kind of catastrophic damage that has become common in recent years. Detailed forecasts of fire paths help teams avoid unnecessary danger and deploy resources more effectively, saving both time and lives. Communities living near forests benefit as well, receiving earlier evacuation notices and facing lower risks to homes, property, and infrastructure.
From a practical standpoint, the system significantly reduces long-term costs. Once installed, it needs little maintenance, and the AI's ability to analyze data automatically means fewer people are required to monitor conditions. Because it can be scaled to suit different areas, from small nature reserves to vast wilderness regions, it provides flexibility and consistent reliability without sacrificing effectiveness.
Even though the AI-driven wireless tree network is already proving its worth, there are areas for improvement and ongoing development ahead. Extending the range of wireless signals to cover denser, larger forests is one of the main technical goals researchers are working on. They are also designing even more durable sensors that can handle extreme weather conditions, resist physical damage, and last longer in the field without maintenance.

Another challenge is integrating this technology into existing firefighting strategies in an effective manner. Fire crews and decision-makers need training to understand the predictions, trust the system, and adjust their plans accordingly. Data security is also a concern. Protecting sensitive information generated by the network is important as these systems expand into more regions and involve multiple agencies.
There is great potential to pair the system with automated firefighting drones or ground vehicles that could react instantly to alerts, addressing fires at their source even faster. The same network might also help monitor other forest concerns, such as detecting illegal deforestation or tracking how wildlife habitats change over time, expanding its value beyond fire defense alone.
The AI-driven wireless tree network represents a new way of protecting forests and communities from wildfires. Instead of waiting until flames are visible, this system allows trees themselves to signal danger through an intelligent, connected network. Combining wireless sensors with AI creates a clear picture of risks in real time, giving responders a chance to act decisively when every second matters. As wildfires grow more frequent and severe, this kind of forward-thinking solution is helping humans and forests coexist more safely. It strengthens our ability to protect lives, homes, and natural ecosystems while respecting the delicate balance of nature. The trees have stood in silent watch over us for centuries. With this technology, they can finally raise their voice when the threat of fire draws near.
Advertisement

Why Gradio stands out from every other UI library. From instant sharing to machine learning-specific features, here’s what makes Gradio a practical tool for developers and researchers
How far can AI go when it comes to problem-solving? Google's new Gemini model steps into the spotlight to handle complex tasks with surprising nuance and range

Discover the top 9 open source graph databases ideal for developers in 2025. Learn how these tools can help with graph data storage, querying, and scalable performance

How to implement Policy Gradient with PyTorch to train intelligent agents using direct feedback from rewards. A clear and simple guide to mastering this reinforcement learning method

GenAI helps Telco B2B sales teams cut admin work, boost productivity, personalize outreach, and close more deals with automation

Discover strategies to train employees on AI through microlearning and hands-on practice without causing burnout.

Discover powerful yet lesser-known ChatGPT prompts and commands that top professionals use to save time, boost productivity, and deliver expert results

Turn open-source language models into smart, action-taking agents using LangChain. Learn the steps, tools, and challenges involved in building fully controlled, self-hosted AI systems
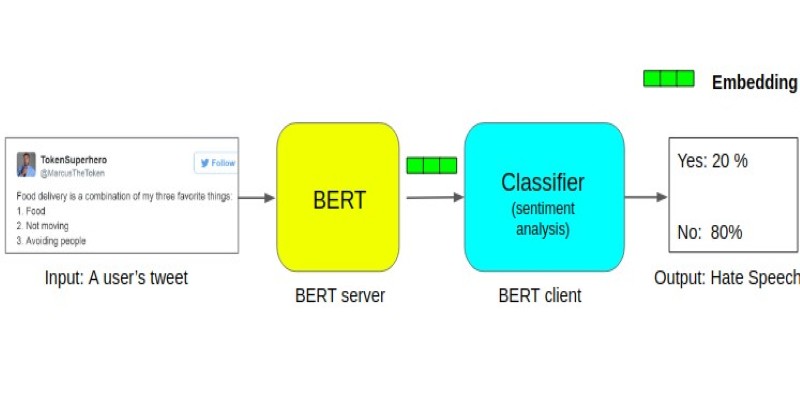
Learn about the BERT architecture explained for beginners in clear terms. Understand how it works, from tokens and layers to pretraining and fine-tuning, and why it remains so widely used in natural language processing

Discover the best Business Intelligence tools to use in 2025 for smarter insights and faster decision-making. Explore features, ease of use, and real-time data solutions
What loss functions are, why they matter, and how they guide machine learning models to make better predictions. A beginner-friendly explanation with examples and insights

Dynamic Speculation predicts future tokens in parallel, reducing wait time in assisted generation. Here’s how it works and why it improves speed and flow